Thunderbolt™ 3 & 4 Explained
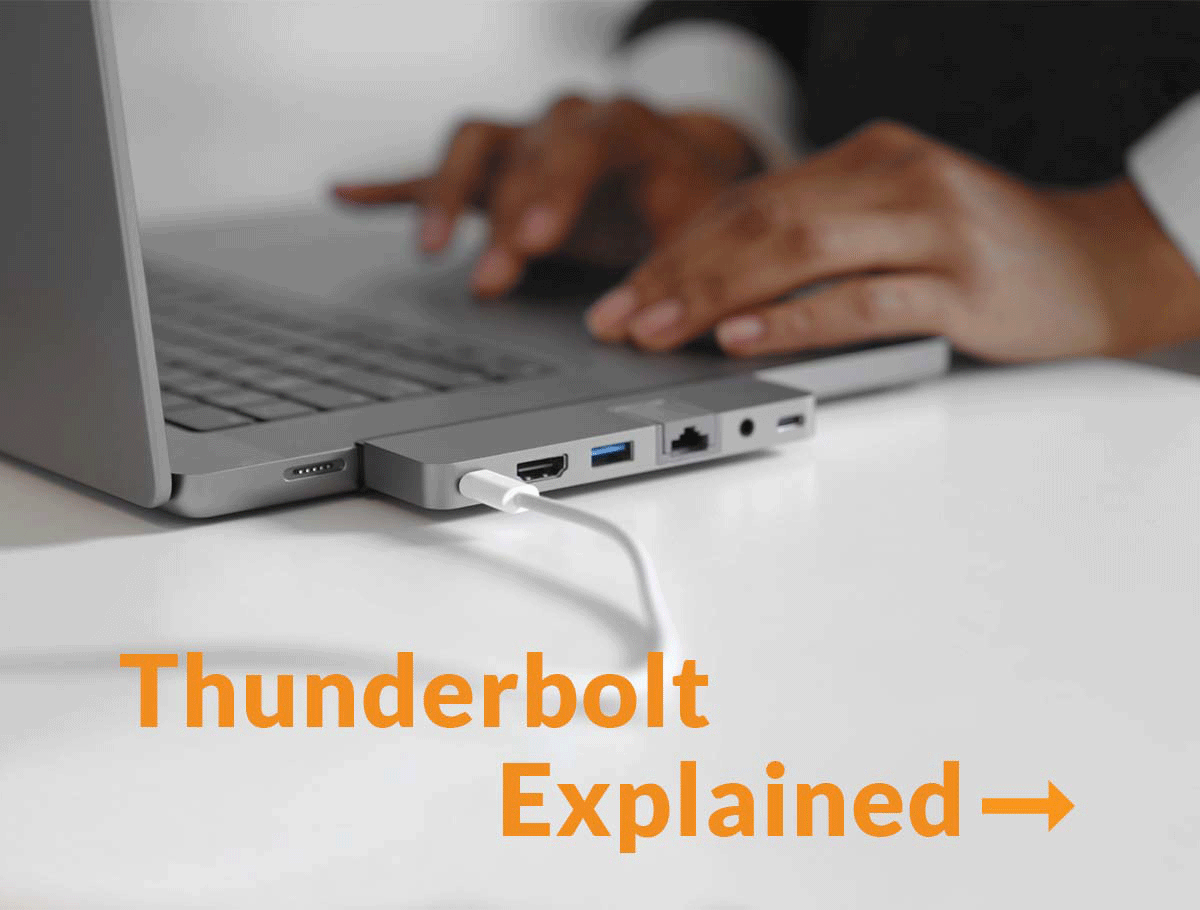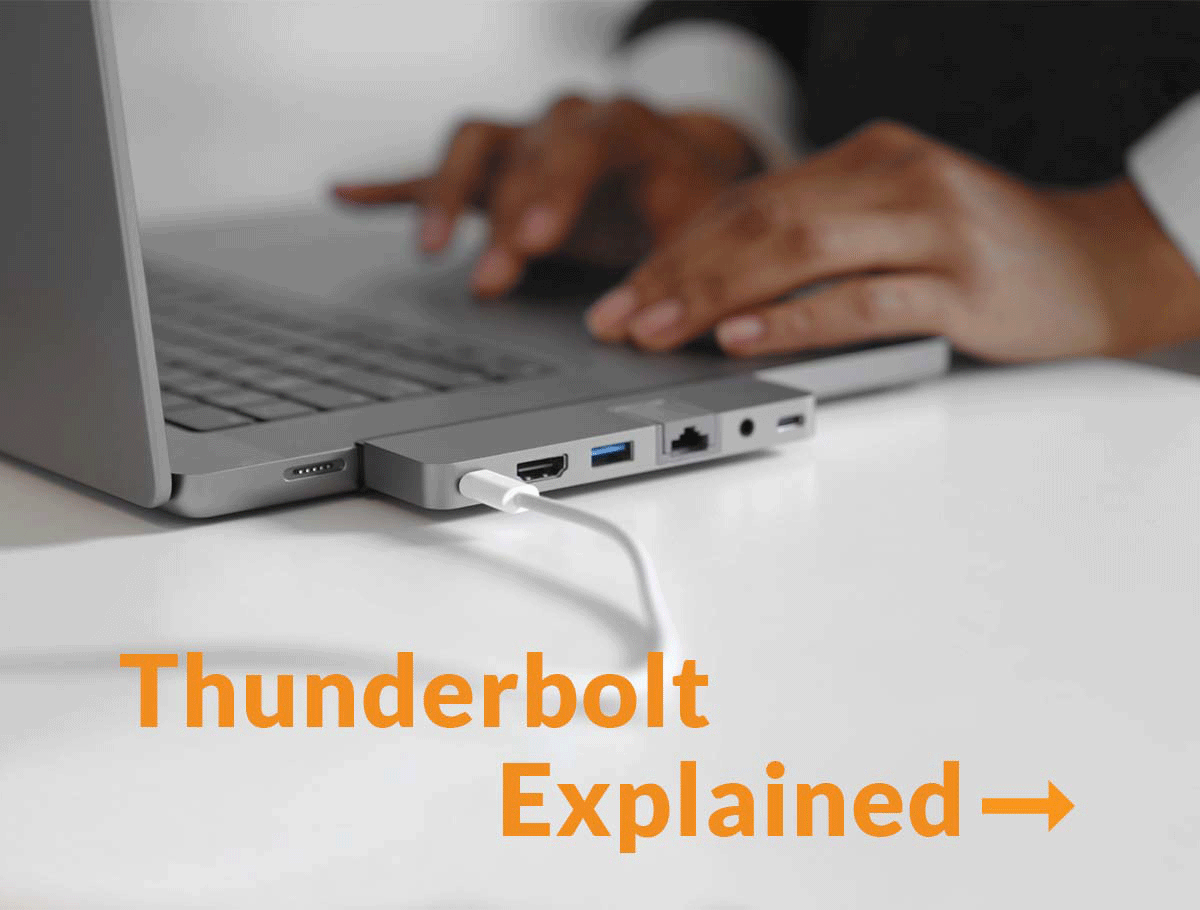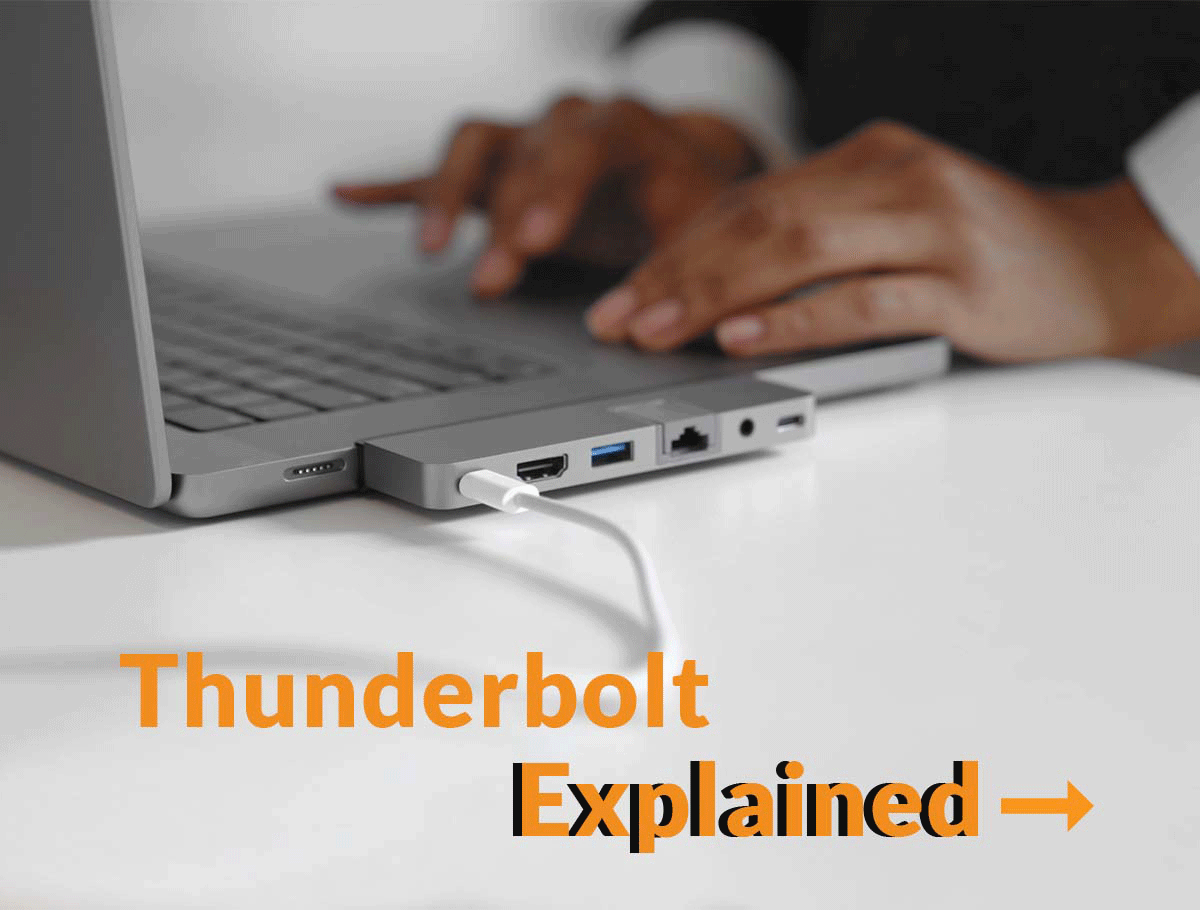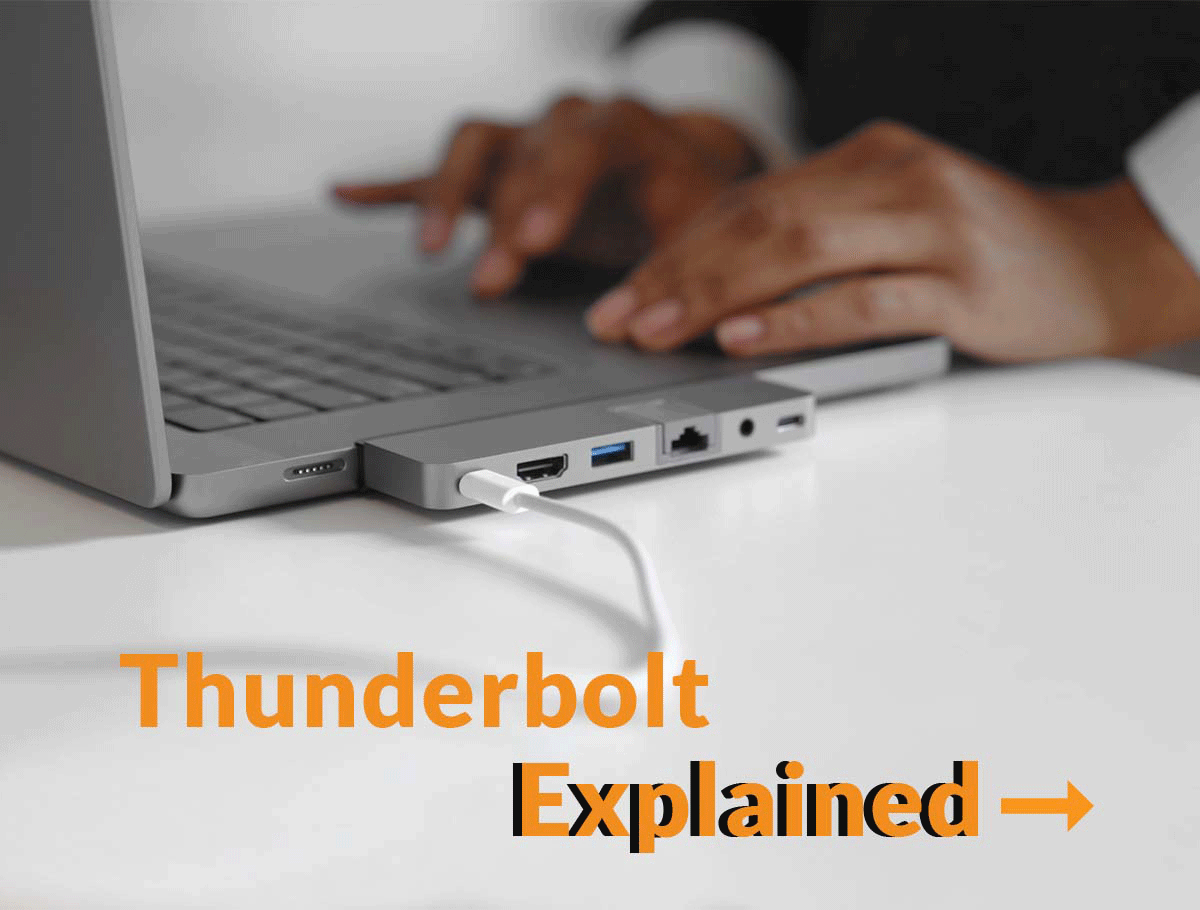
In the universe of connectivity solutions, the past was dominated by numerous variations of a little plug called USB-C. But, over the last several years, there’s an emerging champion for all things data, video and power transfer, and that’s Thunderbolt technology.
But, we’ve heard a lot of questions around Thunderbolt 3 and Thunderbolt 4. So, if you’ve ever found yourself wondering “if Thunderbolt 3 is the same thing as USB-C” or “what do you use Thunderbolt 4 for”, that’s what we’re here to answer.
If you’re looking for more information about USB-C, you can learn more about it in our blog here.
What is Thunderbolt 3?
Thunderbolt, developed by Intel, steps up USB port technology by supporting both high‐speed data and video. To put it bluntly, it’s designed to move large amounts of data quickly and safely between two compatible devices.
- For instance, a laptop expanding high-def video to a display or monitor
- Or, downloading video or photo files from a camera to your laptop
It connects Thunderbolt devices, all HD and 4K displays, and billions of USB-C devices using one compact, reversible cable.
Is Thunderbolt 3 the same as USB-C?
Thunderbolt 3 and USB-C look the same because they share the same port, but they are not the same.
- USB-C refers to the shape of connectors and cables
- Thunderbolt 3 is the technology that runs through the connectors and cables
While all Thunderbolt 3 devices use the USB Type-C port, not all Type-C ports contain Thunderbolt 3 technology. This means that some USB-C ports may not support the features and capabilities of Thunderbolt 3.
Thunderbolt 3 ports look exactly the same as USB-C ports, and indeed, the connector is physically the same from a plug-in perspective. In many cases, they can do everything that a USB-C port can, except much faster.
- Thunderbolt 3 lets you transfer data at up to 40Gbps
- That's twice as fast as 20Gbps found in the quickest USB-C ports
- And four times as fast as the original Thunderbolt
What’s the difference between Thunderbolt 3 & Thunderbolt 4?
At first glance, it's hard to tell the two apart. Both share the standard USB-C connector, and both have a top speed of 40Gbps. In theory, a Thunderbolt 3 device should be able to do just about anything a Thunderbolt 4 device can do.
Compared to version 3, Thunderbolt 4 requires a much stricter set of capabilities to be certified. Take video for example.
- Every Thunderbolt 4 laptop supports two 4K displays or one 8K display
- Whereas Thunderbolt 3 is only required to support one 4K monitor
- Some Thunderbolt 3 ports support two displays at 4K or even one at 8K while others only support one 4K monitor
You can see similar trends in data transfer.
- Thunderbolt 4 requires PCIe at 32 Gbps for storage speeds up to 3,000 Mbps
- Double the minimum requirements of Thunderbolt 3
Unlike Thunderbolt 3, the ability to wake a computer with the shake of a mouse or the tap of a keyboard is now standard on Thunderbolt 4 docks. A small requirement, but one that relieves a lot of annoyance for the end-user.
Thunderbolt 4 also works harder to keep your data safe by requiring Intel VT-d-based direct memory access protection.
What do you use Thunderbolt 4 for?
Thunderbolt 4 is an upgraded cable connection interface from Intel capable of powering your devices, transferring data, and displaying a video source to an external monitor all at once — all with just one port.
Thunderbolt 4 is compatible with plenty of connections or interfaces including:
- DisplayPort
- PCle
- USB4
- It’s even backwards compatible with previous versions of Thunderbolt and connects via USB Type-C
When it comes to speed, Thunderbolt 4 ports have 40Gbps bandwidth. However, Thunderbolt 4 stands out by increasing Thunderbolt 3’s minimum PCIe data requirements from 16Gbps to 32Gbps. That means more room for higher transfer rates and better performance.
For external devices that use PCIe, Thunderbolt 4 will work like a charm.
- Games can be transferred and stored onto an external drive and be played from there, rather than having to transfer the files to the system instead
Last and certainly not least, especially for laptop enthusiasts, Thunderbolt 4 is capable of charging various devices and you won’t need a separate power supply to charge your device.
This includes items like:
- Smartphones
- Laptops that require less than 100W of power
Is Thunderbolt 4 backwards compatible with Thunderbolt 3?
It's backwards compatible, but buying Thunderbolt 4 devices will also future-proof your setup.
So if your Mac has “just” Thunderbolt 3, don’t worry. It’s just that Windows PCs can now join in the fun without limitations, where in the past PC manufacturers could claim theoretical specs but not deliver the best they could by being merely “compatible” rather than “certified”.
Explore our best-selling Thunderbolt 3 Docking Station!
GEN2 16-Port Thunderbolt 3 Docking Station
